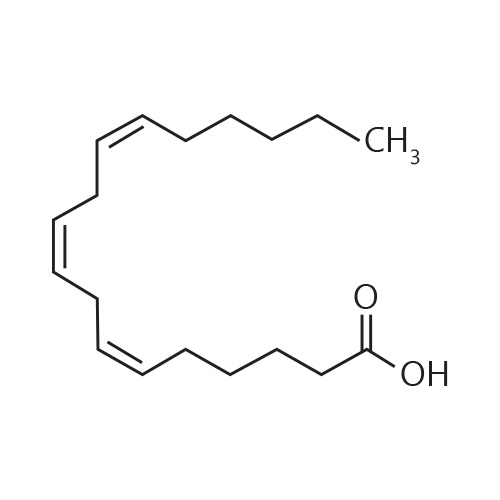
Linolenic Acid
Introduction
Seed oils are the richest sources of linolenic acid: these include canola, soybean, walnut, flaxseed, perilla and evening primrose oils.
Traditional Usage
The body converts linolenic acid into longer chain fatty acids which are thought to lower blood pressure. Other positive effects include anti-inflammatory and anti-blood clotting actions, and lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels. These fatty acids may also reduce the risks and symptoms for other disorders including diabetes, stroke, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, some cancers and mental decline.
*The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.